温馨提示
一、100font收录的所有免费商用字体,在发布之前都经过多方仔细查证,但是,不排除版权方或字体作者某天又修改了授权许可,或者查证过程不小心有疏漏,所以,在实际商用时,建议联系版权方或字体作者再次核实,通过上面 “ 参考资料 ” 里面的链接一般都可以联系到版权方或者字体作者。
注意1:部分免费商用字体,是否可以真正免费商用还存在一些争议;部分免费商用字体有平台限制;部分免费商用字体有时间限制;部分免费商用字体的免费商用范围太小或限制太多;部分免费商用字体的免费商用决心不足或不坚定;请慎重使用。对于上述这些部分免费商用字体,100font不会收录,以免误导。
注意2:100font只收录可以找到资料来源的事实字体,参考资料的意义在于,指出字体的来源与出处,从而保障免费商用是客观真实的。
二、在挑选免费商用字体时,建议优先选择授权分类里的 “ OFL、 Apache、 MIT、GPL、CC0、CC-BY、IPA、字形维基 ” ,这类字体有着明确清晰的授权协议,而且这些协议都是世界知名开源协议,这类字体的免费商用范围非常大、自由度非常高,所以商用安全性也非常高,特别是采用 “ OFL协议 ” 的字体,强烈推荐。
关于作者声明授权:指字体作者或版权方在公开的网络平台(比如官网、微信公众号等)声明字体的授权方式为免费商用。这类字体大部分都没有具体的授权协议,少部分作者或版权方会采用自己编写的协议。这类字体一般无需取得授权文件,也无需知会作者或版权方,直接就可以免费商用,但有少部分字体可能需要先向作者或版权方领取授权文件后,才能进行免费商用,如果需要先领取授权文件,100font在对应的字体详情页里一般会有注明与提醒,请自行与字体作者或版权方联系。
三、100font.com创建于2019年,是一个主要靠爱发电的免费商用字体收集整理网站,致力于让所有人都有免费商用字体使用、让所有人都能正确使用免费商用字体、让所有优秀的公益字体都能得到更有价值的传播,截至目前,甄选后收录的免费商用字体已超过1500款,已累计吸引超700万用户。
若觉得100font对工作学习有帮助,可分享给更多有需要的人,我们的网址是 “ www.100font.com ” ,LOGO 下载
关注 “ 微信公众号(100font) ” 有助于及时了解新字体的发布更新,还有机会获得更多免费商用素材与知识。
四、反馈 / 建议 / 留言:请点击这里,或者发邮件到support@100font.com
一、100font收录的所有免费商用字体,在发布之前都经过多方仔细查证,但是,不排除版权方或字体作者某天又修改了授权许可,或者查证过程不小心有疏漏,所以,在实际商用时,建议联系版权方或字体作者再次核实,通过上面 “ 参考资料 ” 里面的链接一般都可以联系到版权方或者字体作者。
注意1:部分免费商用字体,是否可以真正免费商用还存在一些争议;部分免费商用字体有平台限制;部分免费商用字体有时间限制;部分免费商用字体的免费商用范围太小或限制太多;部分免费商用字体的免费商用决心不足或不坚定;请慎重使用。对于上述这些部分免费商用字体,100font不会收录,以免误导。
注意2:100font只收录可以找到资料来源的事实字体,参考资料的意义在于,指出字体的来源与出处,从而保障免费商用是客观真实的。
二、在挑选免费商用字体时,建议优先选择授权分类里的 “ OFL、 Apache、 MIT、GPL、CC0、CC-BY、IPA、字形维基 ” ,这类字体有着明确清晰的授权协议,而且这些协议都是世界知名开源协议,这类字体的免费商用范围非常大、自由度非常高,所以商用安全性也非常高,特别是采用 “ OFL协议 ” 的字体,强烈推荐。
关于作者声明授权:指字体作者或版权方在公开的网络平台(比如官网、微信公众号等)声明字体的授权方式为免费商用。这类字体大部分都没有具体的授权协议,少部分作者或版权方会采用自己编写的协议。这类字体一般无需取得授权文件,也无需知会作者或版权方,直接就可以免费商用,但有少部分字体可能需要先向作者或版权方领取授权文件后,才能进行免费商用,如果需要先领取授权文件,100font在对应的字体详情页里一般会有注明与提醒,请自行与字体作者或版权方联系。
三、100font.com创建于2019年,是一个主要靠爱发电的免费商用字体收集整理网站,致力于让所有人都有免费商用字体使用、让所有人都能正确使用免费商用字体、让所有优秀的公益字体都能得到更有价值的传播,截至目前,甄选后收录的免费商用字体已超过1500款,已累计吸引超700万用户。
若觉得100font对工作学习有帮助,可分享给更多有需要的人,我们的网址是 “ www.100font.com ” ,LOGO 下载
关注 “ 微信公众号(100font) ” 有助于及时了解新字体的发布更新,还有机会获得更多免费商用素材与知识。
四、反馈 / 建议 / 留言:请点击这里,或者发邮件到support@100font.com
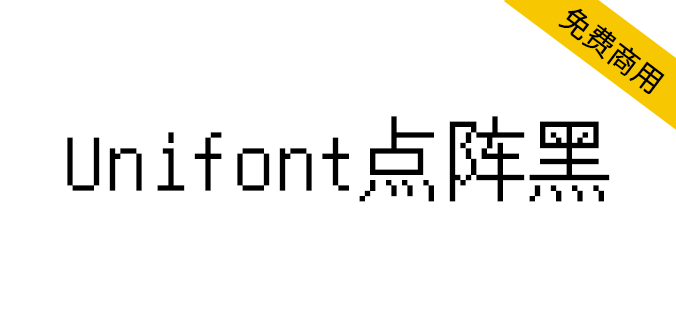
字体颜色
背景颜色
预览
上一个:【峰广明锐体】免费商用字体,心光工作室出品
下一个:【点点像素字体】一款开源免费的中文像素艺术字体